As distance runners, we tend to lean towards the extreme forms of training. We try to run long, pack in one too many extensive speed sessions, and then try to carry out our regular daily activities and obligations. The term “overtraining” is a bit confusing in a sense, since the effects come more from insufficient rest for the particular performance load. Unfortunately the lack of balance between work and rest may actually be decreasing your fitness and risking injury and poor race outcomes. The good news is that there are specific signs you can look out for so you can switch up your program to get out of the rut!
Read moreCan Diet Help Speed Up Injury Recovery?
The worst part about getting injured as an athlete is the thought of the amount of time it will take to get back to our previous fitness level. In order to come back to your healthiest self in the shortest time frame possible, you may want to include a nutritious diet as part of your rehab program. Continue reading to learn why and how to quickly get back to into shape.
Read moreLow Back Pain in Runners: Prevention & Treatment
If you’ve dealt with low back pain, then you know how debilitating it can be to do even the simplest daily activities. Improving core strength, flexibility, and correcting poor body mechanics are the key to managing and preventing pain. Continue reading to learn the exact exercises I prescribe to my clients that lead to maximum relief.
Read moreRecovery: The Key to Improvement
I am sure the majority of distance runners have read a ton of articles about how important recovery is when trying to improve performance. Well, unfortunately many runners learn the hard way when they get injured about how sticking to a recovery routine is absolutely necessary if you want to keep running for a LONG time. I usually say my routine is pretty basic, but in reality, it is actually NOT basic at all. I find myself adding in so many components whenever I do my own research, follow someone who is including some random tactic I have never thought of, or simply when I find myself more tired than usual and realize I need to take a step back. Here are my go-to components I include on a regular basis to keep me injury free and ready for my next workout.
· Diet: For recovery, the focus is usually on that very important post-workout meal; and while that is definitely essential, I believe your diet in general plays a significant role. I got into macro counting a while back and found it to be the best way to eat as an athlete, since it focused on the right mix of carbs, protein, and fats. It was a bit too time-consuming for me, so I no longer count my macros every day, but I do make sure I eat all three (carbs, protein, and fat) in EVERY MEAL. From the protein bars I buy to my restaurant choices, I am conscious about including each macro. This is how I stay satisfied all day! Each of these nutrients play different roles in recovery (more on this in another post), so making sure to be properly fueled with each is vital!
· Sleep & regular “down-time”: While I am definitely not the best sleeper (I am lucky if I can ever reach 7 hours of sleep any night), I do my best to avoid any stressors at night and get to bed early. I also incorporate “down-time” during most of my days where my legs can rest. Getting enough sleep is more important for those of you who have physical jobs that require you to be on your feet all day. Thankfully I work from home for the most part and get enough time to relax…BUT too much of this is not good either! There are days I end up sitting, working on the computer for hours without standing and it actually makes my next day’s run much harder than if I were on my feet all day!
· Compression: Ever since I won my Normatec Recovery System on a social media giveaway, I have been a true fan! I did some research on the benefits of compression for recovery and learned how valuable this can be for athletes. The outcomes are different for everyone I assume, but since using my boots most days of the week, my legs feel much looser in general, I never get my plantar fasciitis pain (and this was a big issue for me!), and my evening runs are much more tolerable.
· Supplements: Although there is no scientific proof that many supplements out there actually work, I have a handful of products I believe have helped me recover faster and feel healthier overall. I take glutamine after every run. This amino acid is usually decreased in the body after any physical or emotional stress (think high intensity workouts, illness, etc.), and plays a role in immune function. Many endurance athletes are more susceptible to catching a cold, and I do not want to deal with one (who has time for that?!), so I do what I can to keep my immune system strong. I also add beetroot powder to my smoothies most days, since it is known to help with stamina and endurance, but it also has loads of antioxidants and other vitamins and minerals that are healthy for the body. Cherry juice has also been a staple in my diet—either in my smoothies or alone at some point during the day. Tart cherries have anti-inflammatory properties, which help reduce soreness and other pain. They are also a natural source of melatonin, which aids in improved sleep quality.
These habits took a while for me to stay consistent with (I am still working on the sleep one!). Besides these components, I also get a massage every few weeks and stretch every day. I have spent a good amount of time on researching about recovery for myself and my clients, so I’ve incorporated more into my routine over the years. My best advice for my athletes is to always listen to your body. Running and training for distance races should not make you exhausted. If it does, then you are definitely missing a component to your recovery routine. Take a step back, switch out running for another easy cross-training activity, and get some rest. It is always best to take a few days off than to deal with an injury.
Periodization Training is Smarter Training
When researching for marathon training plans, you have probably come across the term “periodization”. Basically, the idea behind this training approach is breaking up a training cycle into blocks of about four to eight weeks in length that serve different purposes. It is tough to work on achieving all goals to be marathon-ready all at once, so periodization training has a focus on working on one or two goals at a time. This is most definitely a more realistic training plan for someone who either has limited time to begin with or has several months before their next race. Even elite and professional runners train this way year round. It not only keeps us sane and less stressed working on one thing at a time but also decreases the risk of injuries and burnout.
Periodization Phases
Base
The first phase of periodization training focuses on building endurance, which is the foundation of any long distance running. This is the phase that builds up mileage using gradually increasing easy runs with only a few short speedier runs mixed throughout. The speed work during the base phase should include of 10 to 20 sets of 20 to 30-second strides at the end of a few easy runs each week. Strides are useful for working on proper running form and to prepare the body for faster running. Each set should be a gradual pick-up in speed to a controlled fast pace while working on increasing your stride length. Performing strides on grass decreases the impact on the body.
Another addition of speed work during the second half of the base phase is the inclusion of mini tempo runs. Pick one easy run per week to include 15 minutes of running at around half marathon pace. This will begin introducing faster paced running so that the next phase of your training cycle will not be too shocking. Weekly long runs are the cornerstone of phase one and should always be done at conversational pace and build up to about 15 to 16 miles in length. Two to three days per week of weight training should also be included in this phase to build strength in important muscle groups such as the legs and core. Since the base phase is the easiest on the body, it can be anywhere from four to eight or more weeks in length.
Strength
The second phase of periodization training focuses on building strength and speed with the inclusion of more specific speed workouts and hill sessions while maintaining mileage and weight training. In this phase, two easy runs per week will turn into two different speed sessions. The first speed session should be an increasing tempo run. Start with 15 minutes of your run at half marathon pace or slightly faster the first week and increase by 5 to 10 minutes each week until you are running 60 minutes at tempo pace. These workouts will help build strength in connective tissue and build muscle endurance to be able to get comfortable with running at your goal pace.
The second speed session can be alternated between shorter, faster repeats and hill workouts. Running on a track works best, but any uninterrupted road will do. After warming up for two to three miles, run intervals such as 4 to 8 repeats of between 1000 to 1600 meters at 5k to 10k race pace with short recovery periods of 1 to 2 minutes in between. Cool down for one or two miles. Every other week can include hill repeats of both uphill and downhill running at half marathon pace. Begin with four sets and build to eight to ten repeats by the end of the phase. Hill workouts are an excellent lower impact way to build strength and speed. Phase two will last about eight weeks in length.
Peak
The peak phase of periodization training is basically where your highest mileage and hardest workouts land. This is where you build confidence and tax your body the most while continuing to build fitness. With proper periodization, you should feel comfortable running at your goal pace for several miles during peak month. Continue with two speed workouts each week—one longer tempo run and shorter, faster repeats. Your track session will include double the repeats you were doing in the strength phase with distances ranging from 200 to 800 meters at 5k pace with one or two recovery minutes in between, for example. Form drills and strides should not be neglected during this phase, as it is a time to practice maintaining proper mechanics when fatigued.
Following the peak phase is two weeks of tapering right before your race. After this tough month of your hardest training, your body will beg for the taper weeks. Many runners usually dread these couple of weeks before a race because they feel they are losing fitness with the scaling back of volume and intensity. With proper phasing in training, you can push your limits during the peak phase and enjoy your taper, as you should. It is a time to let your body recover and focus on good nutrition and sleep to gather energy for race day. Periodization is a useful method to plan your training as it helps to gradually adjust your body to higher intensity and faster paces with a lower risk of overtraining or injuries. You are less likely to experience any setbacks during training using these cycles.
Sources
Trent Stellingwerff, Case Study: Nutrition and Training Periodization in Three Elite Marathon Runners, Journal, July 22, 2020.
Got Shin Splints? Learn How to Treat & Prevent This Annoying Injury
One of the most annoying, but significantly common, running injuries is shin splints. Well, this is the usual diagnosis from a doctor or other medical professional when you tell them you have pain in the front part of your lower leg, even without examining you first. Besides learning how to treat and prevent this issue, it is important for athletes to understand the symptoms and different diagnoses that are associated with shin splints in the first place, since there are other similar injuries that can be career (and life!) threatening.
“Shin Pain” Causes
The number one cause of pain in the shins is overuse. You will hear from many doctors and physical therapists that biomechanical factors—think: flat feet, heel striking and overpronating, are the main cause, but it actually has more to do with overloading in general. Yes, these factors contribute to pain and other problems, but without the “overuse” part, most injuries wouldn’t occur. When it comes to runners, those who skip strength training and run excessively are more prone to any overuse injuries. It can be difficult to keep up with other exercises when your mileage builds up and you have a life outside of running, but this is when it is most important.
Differential Diagnosis
A specific condition that often times gets overlooked when diagnosing shin splints is compartment syndrome. Although distance runners will have the less dangerous type—chronic compartment syndrome, it is important to note the symptoms of the acute version, which can be life threatening. This condition consists of increased pressure in the lower limbs from “trapped” fluid. It mimics shin splints in the sense that there is achiness in the shin bone and surrounding areas during activity. With compartment syndrome, this pain rapidly worsens during activity and almost feels like “congestion” in the lower limbs. If you are experiencing similar symptoms, DO NOT continue running and seek medical care as soon as possible!
Stress fractures are often times caused by prolonged shin splints due to the increased use of already inflamed muscles and weakening of the tibia (shin bone). This weakening is the result of degeneration of the bone from overuse. Proper treatment of shin splints can lead to a fast recovery, but it is not the case with a stress fracture. Training through shin pain to the point that it leads to a stress fracture will only delay your progress and cause you to sit out of running for months.
Treating Shin Splints
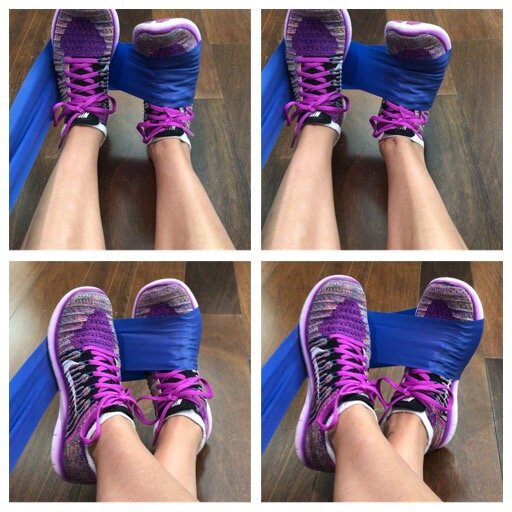
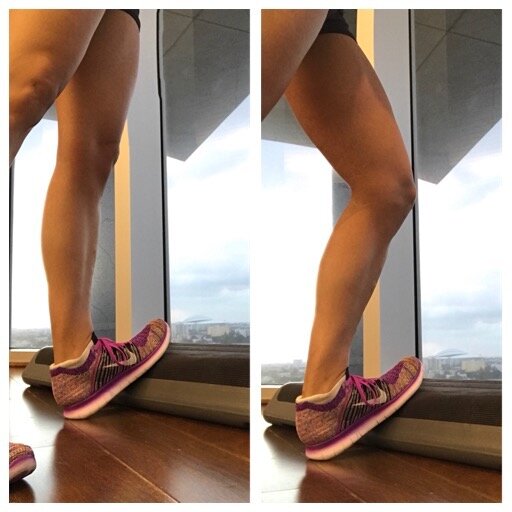
The first step to recovery is rest (as it is with almost every injury). Start by taking a few days off and icing the area of pain three times per day if you can. Initially it is best to figure out what caused your shin splits to begin with, which is usually a combination of tight calf muscles, weak lower leg and ankle muscles, and inefficient strength of muscles higher up in the body such as the knees, hips, and core. Once the pain is under control and any swelling has relieved, then a gradual progression of strengthening and flexibility exercises should be incorporated. Below are simple ankle exercises used to strengthen the muscles that run down the entire lower leg, as well as stretching techniques for both groups of calf muscles.
When easing back into running, it is a good idea to rotate between different types of shoes throughout the week. Alternating surfaces is also helpful. Try switching between the road, grass, treadmill, and track to relieve pressure in different areas of the feet and legs. For runners who overpronate, choose shoes that help correct your foot strike, or wean into a pair of orthotics that help align your feet. Of course, if any pain starts to trickle back into the picture, take a few days off, ice, and keep working on the exercises. You should always continue strengthening and stretching a few times per week, even if your treatment is successful, in order to prevent shin splints and many other problems in the future.
Physical Therapists: The Experts of Movement
Pain or injury can strike just about anyone at any stage in life. Whether you are a professional athlete, weekend warrior, or even a sedentary person, your body can suffer aches, strains, overuse, or accidental injuries with any move you make. The good thing is for most of the everyday aches and pain many go through, as well as muscular and joint-related injuries, a physical therapist can come to the rescue.
Not only can physical therapists help with hands-on techniques to relieve pain and improve joint and muscle mobility, but they are well-educated in exercise rehabilitation for the prevention of issues in the future. You can definitely learn helpful tips from these professionals on how to keep your body healthy and be stronger at your sport of choice. There are many physical therapists who specialize in orthopedic problems as well as sports-related injuries. This may come in handy for those who have experienced issues with injuries resulting from poor posture and mechanics, or specific weaknesses in certain muscle groups.
Manual Therapy
Soft tissue injuries usually require some form of hands-on therapy to relieve stiffness in joints, tightness in muscles, or scar tissue development from surgery or old injuries. Many people think that physical therapy is just about massage and stretching, but it is the conjunction of these techniques with exercises that relieve pain and dysfunction for the long term. If a therapist solely uses a joint mobilization technique to increase the range of motion of a shoulder, for example, the stiffness will just return if no exercises are used to strengthen the joint to remain in that loosened position.
The massage used in physical therapy is not your typical massage you get at the spa. Soft tissue mobilization is the proper term and is used specifically for loosening tight muscles and tendons, especially at their connections to the bones, as well as for flushing out toxins and inflammation to relieve pain and improve movement. It is not typical for a physical therapist to be spending more than 10 or 15 minutes “massaging” one area. This technique is frequently used as part of a warm-up for exercises and stretching.
Specialty Techniques
Active Release
You have probably heard of ART before, which is a common form of therapy used by physical therapists, chiropractors, and massage therapists. This form of massage is where deep pressure is applied to an area of tightness or pain while instructing the patient to actively move as if stretching the area. This technique, by no means, feels good as most massage does. The patient will usually feel an uncomfortable stretching sensation. ART helps to break up any adhesions and scar tissue that is causing limitations in mobility.
Graston Technique
This form of soft tissue mobilization uses an instrumental tool to produce microtrauma to an area that already has scar tissue and adhesions present. It may not make sense to cause further injury to an area, but it will actually restart the healing process by increasing blood flow and supply the nutrients needed to properly heal the area. Studies have shown that many common running-related injuries respond well to the Graston method such as Achilles tendonitis, runner’s knee, plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and hip flexor strains.
Dry Needling
Similar to acupuncture, this technique has more recently been used by physical therapists to address trigger points in the body. Trigger points are usually sensitive to the touch and may sometimes produce pain in other areas of the body. Dry needling does not use any form of medication along with the injection and can be performed superficially or deep in the affected tissue. The idea is that this needle injection helps release the tension in the trigger point to improve pain and relax the nerves that are transmitting the pain impulses to the muscles. Therapists can actually feel the extent of tightness in muscles, which is invisible to other diagnostic tools such as MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays.
Exercise
The treatment approach of exercise is the most important part of physical therapy as it is what will bring long-term results. Manual therapy and modalities, including hot and cold pack treatment, will usually only provide temporary pain relief and joint mobility. Without the exercise portion of physical therapy, your body will just return to its original state of joint limitation and muscle tension once you resume your regular activities. Physical therapists are the experts in exercise for flexibility and strengthening, as well as the safe transition back into your sport. Unlike personal trainers, physical therapists are highly trained in injury prevention and can guide patients with a healthy approach to returning to their activities. For these reasons, when choosing a trainer to help you get into shape, a physical therapist may be a better option over a certified personal trainer.
Sources:
1American Physical Therapy Association, The PhysicalTherapist’s Guide to Healthy Running, Website, Jul 08, 2018
James Dunning, Raymond Butts, Firas Mourad, Ian Young, Sean Flanagan, and Thomas Perreault, Dry Needling: A Literature Review with Implications for Clinical Practice Guidelines, Journal, Jul 08, 2018