The worst part about getting injured as an athlete is the thought of the amount of time it will take to get back to our previous fitness level. In order to come back to your healthiest self in the shortest time frame possible, you may want to include a nutritious diet as part of your rehab program. Continue reading to learn why and how to quickly get back to into shape.
Read moreGot Shin Splints? Learn How to Treat & Prevent This Annoying Injury
One of the most annoying, but significantly common, running injuries is shin splints. Well, this is the usual diagnosis from a doctor or other medical professional when you tell them you have pain in the front part of your lower leg, even without examining you first. Besides learning how to treat and prevent this issue, it is important for athletes to understand the symptoms and different diagnoses that are associated with shin splints in the first place, since there are other similar injuries that can be career (and life!) threatening.
“Shin Pain” Causes
The number one cause of pain in the shins is overuse. You will hear from many doctors and physical therapists that biomechanical factors—think: flat feet, heel striking and overpronating, are the main cause, but it actually has more to do with overloading in general. Yes, these factors contribute to pain and other problems, but without the “overuse” part, most injuries wouldn’t occur. When it comes to runners, those who skip strength training and run excessively are more prone to any overuse injuries. It can be difficult to keep up with other exercises when your mileage builds up and you have a life outside of running, but this is when it is most important.
Differential Diagnosis
A specific condition that often times gets overlooked when diagnosing shin splints is compartment syndrome. Although distance runners will have the less dangerous type—chronic compartment syndrome, it is important to note the symptoms of the acute version, which can be life threatening. This condition consists of increased pressure in the lower limbs from “trapped” fluid. It mimics shin splints in the sense that there is achiness in the shin bone and surrounding areas during activity. With compartment syndrome, this pain rapidly worsens during activity and almost feels like “congestion” in the lower limbs. If you are experiencing similar symptoms, DO NOT continue running and seek medical care as soon as possible!
Stress fractures are often times caused by prolonged shin splints due to the increased use of already inflamed muscles and weakening of the tibia (shin bone). This weakening is the result of degeneration of the bone from overuse. Proper treatment of shin splints can lead to a fast recovery, but it is not the case with a stress fracture. Training through shin pain to the point that it leads to a stress fracture will only delay your progress and cause you to sit out of running for months.
Treating Shin Splints
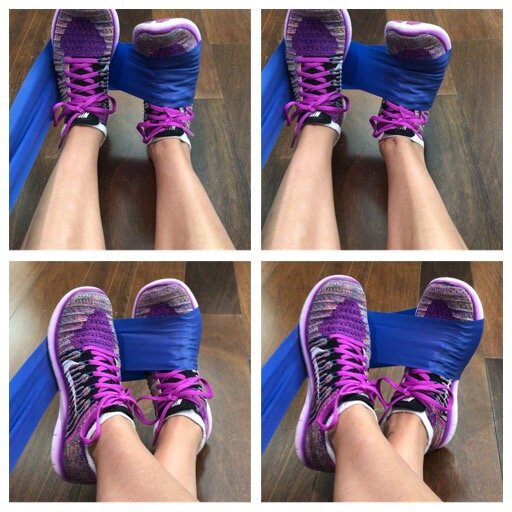
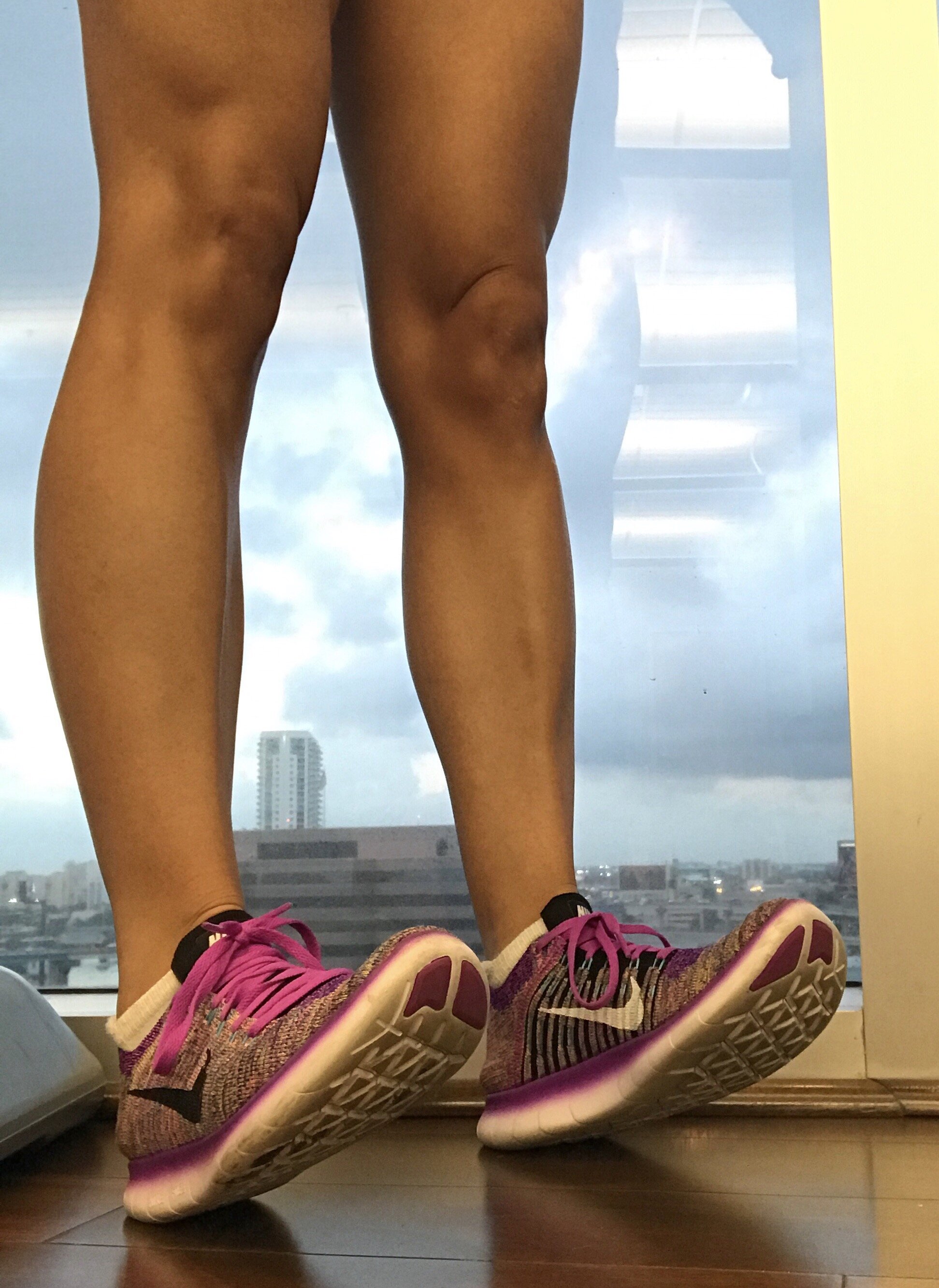
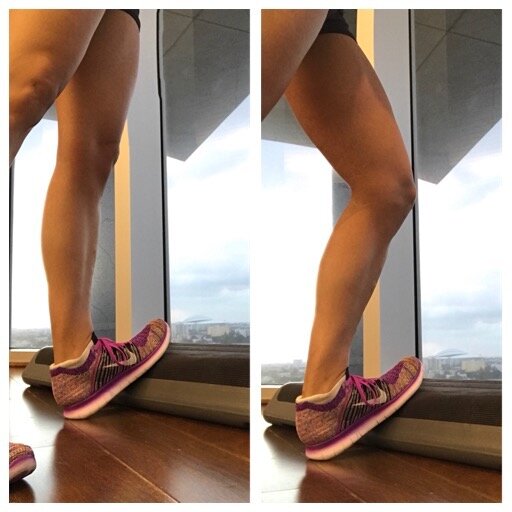
The first step to recovery is rest (as it is with almost every injury). Start by taking a few days off and icing the area of pain three times per day if you can. Initially it is best to figure out what caused your shin splits to begin with, which is usually a combination of tight calf muscles, weak lower leg and ankle muscles, and inefficient strength of muscles higher up in the body such as the knees, hips, and core. Once the pain is under control and any swelling has relieved, then a gradual progression of strengthening and flexibility exercises should be incorporated. Below are simple ankle exercises used to strengthen the muscles that run down the entire lower leg, as well as stretching techniques for both groups of calf muscles.
When easing back into running, it is a good idea to rotate between different types of shoes throughout the week. Alternating surfaces is also helpful. Try switching between the road, grass, treadmill, and track to relieve pressure in different areas of the feet and legs. For runners who overpronate, choose shoes that help correct your foot strike, or wean into a pair of orthotics that help align your feet. Of course, if any pain starts to trickle back into the picture, take a few days off, ice, and keep working on the exercises. You should always continue strengthening and stretching a few times per week, even if your treatment is successful, in order to prevent shin splints and many other problems in the future.
Running with Arthritis? Here's All You Need to Know to Stay Healthy
One of the most common complaints of pain for most adults is caused by arthritis. This condition can become extremely debilitating and limit the ability to enjoy even the simplest activities. It has been a common thought that running is harmful to joints and causes arthritis. Recent research has shown the opposite results. Running can actually help control the symptoms of arthritis. Early signs are often ignored as they are usually short-lived and infrequent and can mimic other conditions such as overuse symptoms and muscle soreness. If you are a runner or partake in other activities, it is beneficial to understand the causes, symptoms, and management options available in order to avoid requiring invasive treatment.
What is Arthritis?
According to the Arthritis Foundation, the condition is just a term used to described joint disease and includes over 100 different types. It is most common in adults, but many of these types of arthritis can be found in children, as well. The cartilage located in between bones, which acts as a “cushion”, is lost creating constant pressure during activities. The earliest symptoms include joint stiffness, pain, and swelling. As mentioned, these can last a short time and occur infrequently. Stiffness is usually felt the most after prolonged positioning such as sitting or when getting out of bed in the morning. When in motion, the stiffness is usually relieved. In more advanced stages of arthritis, significantly prolonged activities can make the pain worse. Over time, arthritis can cause visible joint changes such as enlarged knuckles. Other joint deformities are only visible with X-rays.
Unfortunately, arthritis cannot be cured, but there are several management strategies available that can allow you to live comfortably without sacrificing your desired activities. The most important treatment approach, especially in the early stages, is balancing aggravating activities with rest. The key is to control the buildup of inflammation in order to avoid extreme pain to the point where you must take too much time off. For runners, this means if you are beginning to feel symptoms during or after a 10-mile run or longer, than you should be cutting back to shorter runs and adding in other cross-training activities, including strength training.
Strength Training is a Must
The constant grinding of bones with arthritis is what naturally causes pain and swelling. Getting the surrounding muscles stronger can help relieve this pressure. Stronger muscles also mean you can tolerate activities for a longer period of time, such as getting back to those 10-mile runs and racing marathons. Yes, this is possible, but runners must understand that strength training needs to become part of their regular training regimen. It is also the best way for non-runners to help control their symptoms and possibly avoid worsening arthritis and requiring surgery.
For hip and knee arthritis, which is one of the most common areas affected, especially in runners, it is important to alternate between bodyweight and resistance exercises. Both offer strength gains but give the joints a break from too much impact. Exercises should incorporate the larger muscle groups such as the quads, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, as well as smaller muscles that play a role in hip and knee stabilization. These smaller groups are the hip abductors and adductors, internal and external rotators, and the core muscles. Besides squats, lunges, heel raises, and step-ups, which all target the larger muscle groups, floor exercises for the lower body are an easy way to get in strength training at any time. Bridges, clamshells, and hip extensions are all great exercises that can be done with or without a resistance band. Core exercises such as planks and leg raises are also good additions.
Management for Runners
Besides alternating runs with lower impact cross training, there are several other strategies to help relieve symptoms. Using hot packs before activities can help ease pain and stiffness and the use of ice afterward can help control inflammatory buildup from your workout. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can also help manage symptoms. Below are other methods specifically for runners with arthritis.
Use a run-walk method during most runs
Eat a low-inflammatory diet. Examples of foods that help lower inflammation in the body include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, beans, and fish. Foods that can increase inflammation include fried foods, high gluten foods, processed and high-fat meats, dairy products, and foods with trans fats.
Run on softer surfaces. Consistent road running causes repetitive pounding on joints. Try alternating running on trails, grass, and the treadmill.
Warm-up properly. Getting right into running on stiff joints can exacerbate symptoms. Incorporate dynamic stretches such as leg swings, lunges, hamstring and quad pulls, and ankle rolls before every run.
Exercise consistently. Avoid taking long breaks in between workouts. Even if you do not have time for your training runs due to a busy work and family schedule, you can increase the amount of walking during the day by parking further from your destination, stretching while cooking dinner, or waking up 15 minutes earlier to add in a few exercises before starting your day.
Sources
Paul T. Williams, Effects of Running and Walking on Osteoarthritis and Hip Replacement Risk, Journal, Sep 2019
Ponzio DY, Syed UAM, Purcell K, Cooper AM, Maltenfort M, Shaner J, Chen AF, Low Prevalence of Hip and Knee Arthritis in Active Marathon Runners, Journal , Sep 2019
Arthritis Foundation, What is Arthritis?, Website, Sep 2019